Create an Incremental Python Transform
In this guide, we'll build an Incremental Python Transform that processes only new or changed data to improve pipeline performance.
Check out our concept guides to learn about incremental processing strategies and supported input formats.
Prerequisites
- Ascend Flow
Create a Transform
You can create a Transform in two ways: through the form UI or directly in the Files panel.
- Using the Component Form
- Using the Files Panel
- Double-click the Flow where you want to add your Transform
- Right-click on an existing component (typically a Read component or another Transform) that will provide input data
- Select Create Downstream → Transform
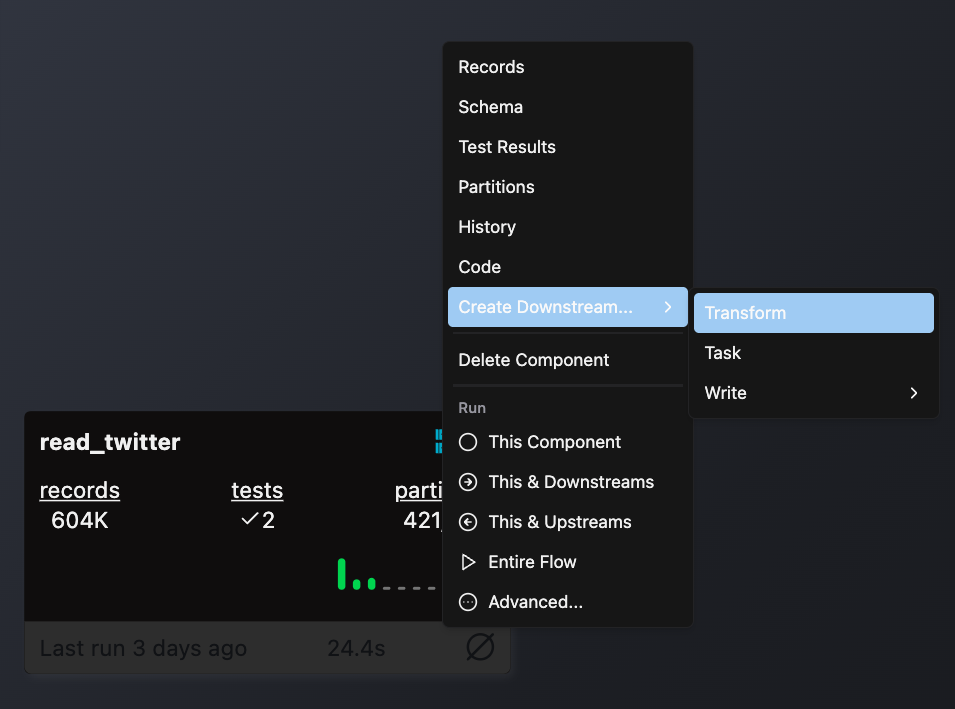
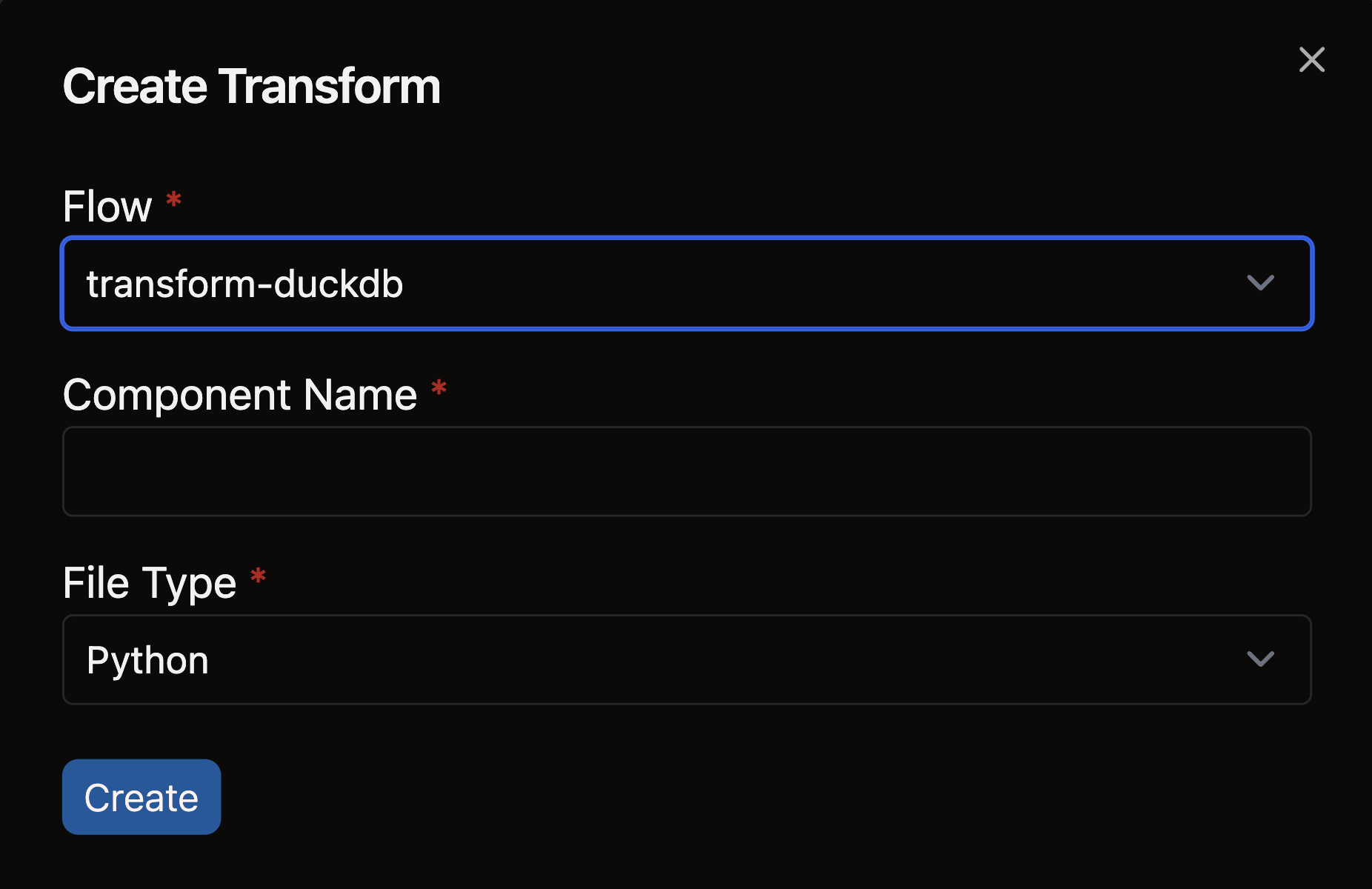
- Complete the form with these details:
- Select your Flow
- Enter a descriptive name for your Transform (e.g.,
sales_aggregation) - Choose the appropriate file type for your Transform logic
- Open the files panel in the top left corner
- Navigate to and select your desired Flow
- Right-click on the components directory and choose New file
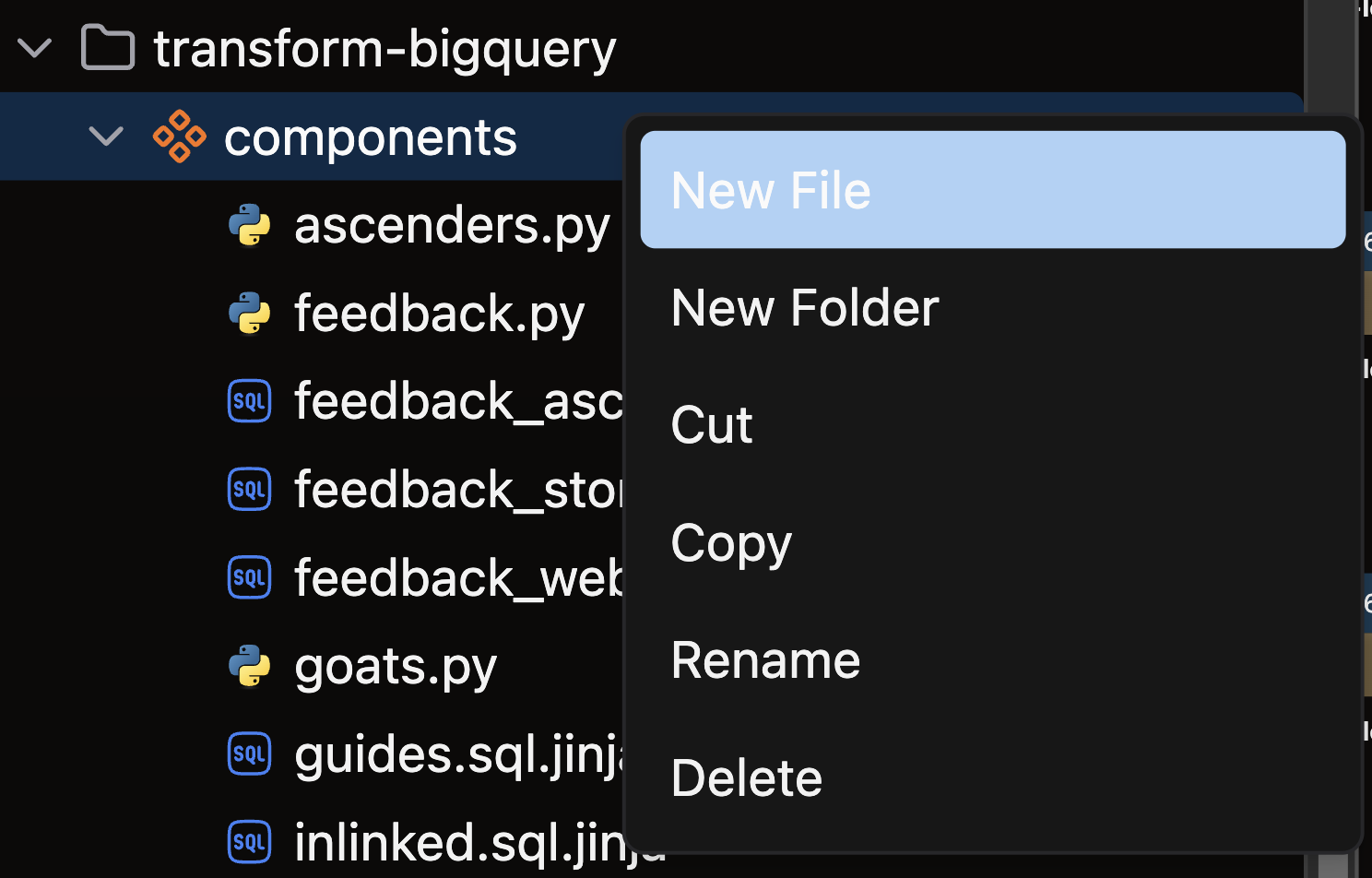
- Name your file with a descriptive name that reflects its purpose (e.g.,
sales_aggregation) - Choose the appropriate file extension based on your Transform type:
.pyfor Python Transforms.sqlfor SQL Transforms
Create your Python Transform
Structure your Python Transform following this pattern:
-
Import necessary packages: Import Ascend resources like
transformandreffrom theascend.resourcesmodule -
Apply the
@transform()decorator: Configure it with:inputs: List of input datasets usingref()materialized: Set to"incremental"to enable incremental processingincremental_strategy: Use"merge"for updating existing recordsunique_key: Specify a column that uniquely identifies recordsmerge_update_columns: List columns that should be updated during merges
-
Define your transform function: Create a function that takes input data and
contextparameters -
Use incremental context: Check
context.is_incrementaland usecontext.current_data()to access existing data -
Filter for new data: Use incremental state to process only new or changed records
- Compare current data with previous state using timestamps or IDs
# Example of filtering for new data
if context.is_incremental:
current_data = context.current_data()
# Only process records with newer timestamps
output = output[output["timestamp"] > current_data["timestamp"].max()] -
Return the processed data: Send your transformed data back to Ascend
- Return a properly structured dataframe or table object
Example
This example demonstrates how to create an incremental transform that only processes new or updated records:
"""
Example of an Incremental Python Transform Component.
This file demonstrates how to create a transform that processes only new or
changed data to improve pipeline performance using the incremental strategy.
"""
from ascend.resources import ref, transform
@transform(
inputs=[ref("incrementing_data")],
materialized="incremental",
incremental_strategy="merge",
unique_key="key",
merge_update_columns=["string", "ts"],
)
def incremental_transform_python(incrementing_data, context):
"""
Process only new or updated records from the input dataset.
This function demonstrates incremental processing using the merge strategy.
It identifies records that have changed since the last run and only processes
those, significantly improving performance for large datasets.
Args:
incrementing_data: Input dataset with new/changed records
context: Component execution context with incremental state information
Returns:
Processed dataset containing only new/changed records
"""
def _n(x):
"""Helper to handle column name differences between data planes."""
return x if "string" in incrementing_data else x.upper()
# Start with all input data
output = incrementing_data
# If we're running incrementally (not the first run)
if context.is_incremental:
# Get previously processed data
current_data = context.current_data()
# Filter for only records newer than what we've already processed
# This is the key to incremental processing - only work on new data
output = output[output[_n("ts")] > current_data[_n("ts")].max()]
return output
🎉 Congratulations! You've successfully created an Incremental Python Transform in Ascend.