Create a Simple Python Transform
In this guide, we'll build a Simple Python Transform that processes data without using Incremental or Smart Partitioning strategies.
To learn more about the supported input formats for Python Transforms, check out our concept guide.
Let's keep it Simple!
Prerequisites
- Ascend Flow
Create a Transform
You can create a Transform in two ways: through the form UI or directly in the Files panel.
- Using the Component Form
- Using the Files Panel
- Double-click the Flow where you want to add your Transform
- Right-click on an existing component (typically a Read component or another Transform) that will provide input data
- Select Create Downstream → Transform
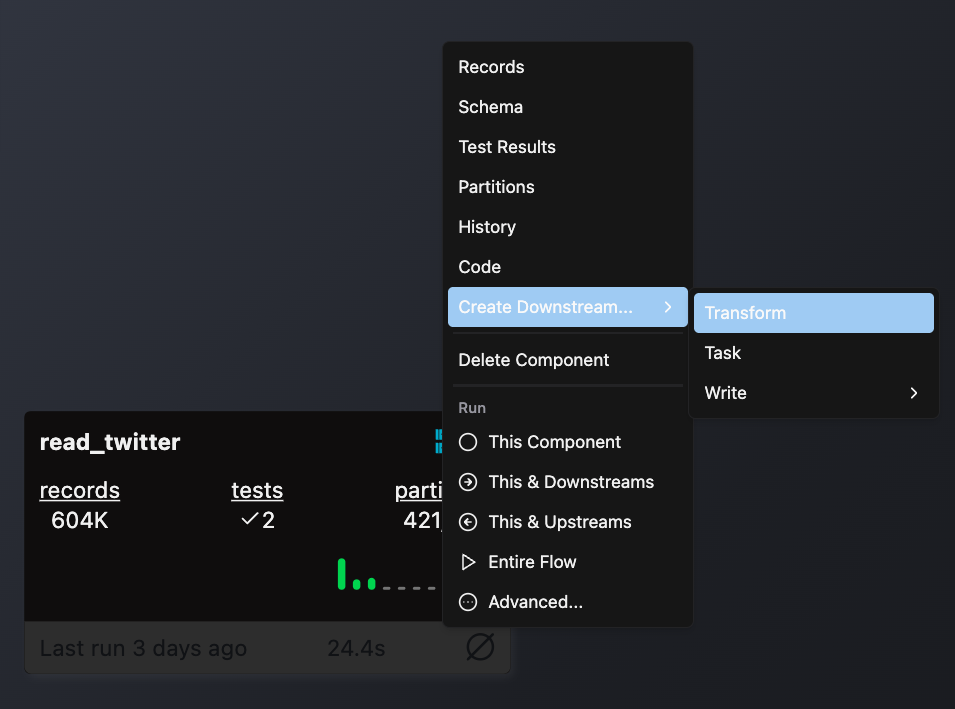
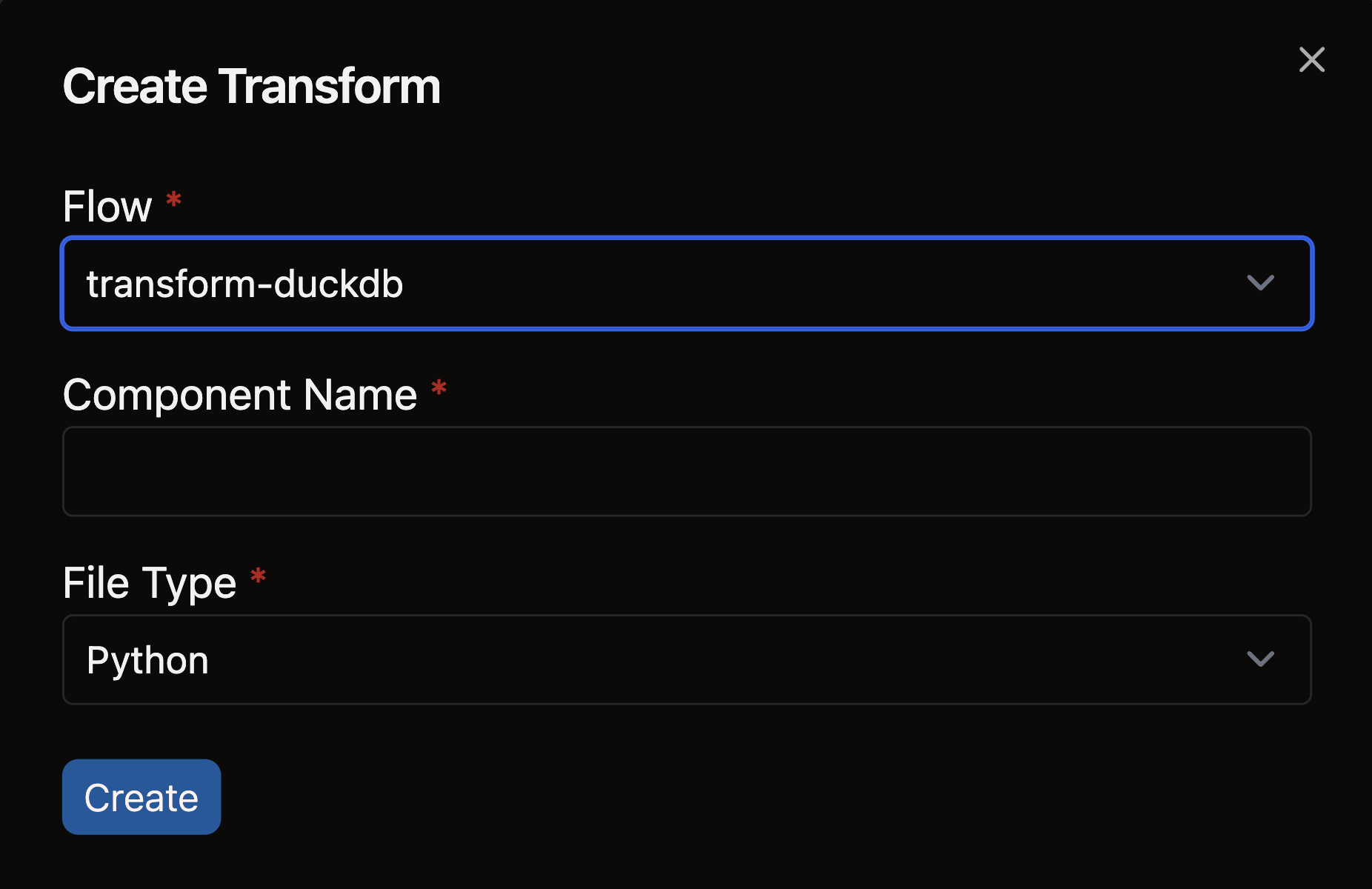
- Complete the form with these details:
- Select your Flow
- Enter a descriptive name for your Transform (e.g.,
sales_aggregation) - Choose the appropriate file type for your Transform logic
- Open the files panel in the top left corner
- Navigate to and select your desired Flow
- Right-click on the components directory and choose New file
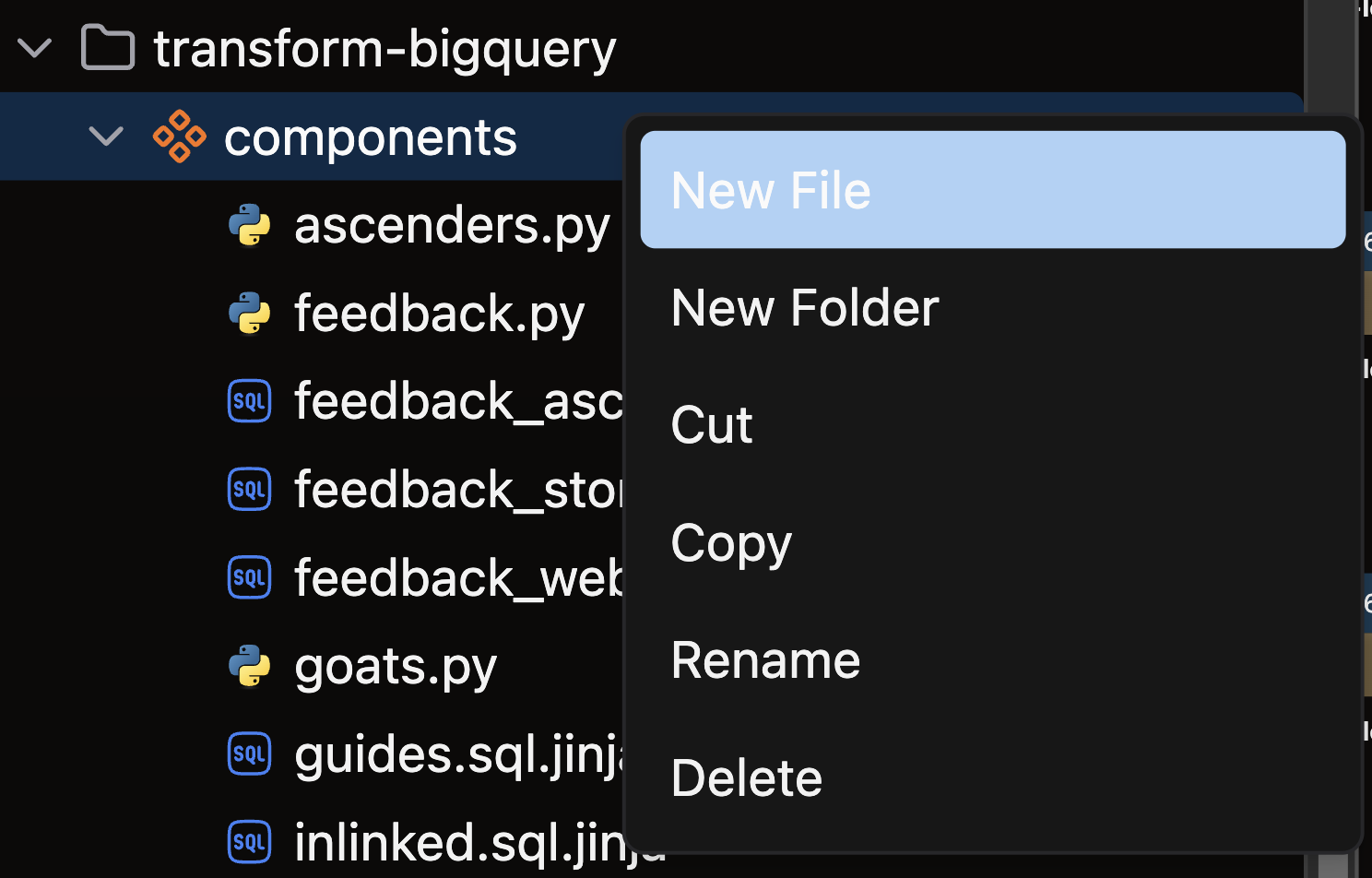
- Name your file with a descriptive name that reflects its purpose (e.g.,
sales_aggregation) - Choose the appropriate file extension based on your Transform type:
.pyfor Python Transforms.sqlfor SQL Transforms
Create your Python Transform
Structure your Python Transform Component following this pattern:
- Import necessary packages: Include Ascend resources (
transform), context handlers (ComponentExecutionContext), and data processing libraries (likeibisin this example) - Define your transform function: Create a function that performs some transform action on your data (cleaning in this example)
- Apply the
@transform()decorator: Use your desired input refs. This transforms your function's output into Ascend's internal data format - Return structured data: Ensure your function returns a dataframe or table
The @transform() decorator handles the conversion between your Python data structures and Ascend's internal format, enabling seamless integration with downstream components in your data pipeline.
Example
Here's a simple example that shows how to transform input data by applying cleaning operations:
"""
Example of a Simple Python Transform Component.
This file demonstrates how to create a basic Python transform that processes
data without using Incremental or Smart partitioning strategies.
"""
import ibis
from ascend.application.context import ComponentExecutionContext
from ascend.resources import ref, transform
@transform(inputs=[ref("read_weather_routes", flow="extract-load-duckdb")])
def weather_routes(read_weather_routes: ibis.Table, context: ComponentExecutionContext) -> ibis.Table:
"""
Transform weather routes data by applying cleaning operations.
Args:
read_weather_routes: Input table containing weather route data
context: Component execution context
Returns:
Cleaned weather routes table
"""
# In a real implementation, you would import your cleaning function from a module
# This is a placeholder for demonstration purposes
weather_routes = clean_weather_data(read_weather_routes)
return weather_routes
def clean_weather_data(data: ibis.Table) -> ibis.Table:
"""
Clean weather data by removing nulls and standardizing column formats.
Args:
data: Raw weather routes data
Returns:
Cleaned data
"""
# Example cleaning operations
# In a real implementation, you would have actual cleaning logic here
cleaned_data = data.filter(data.route_id.notnull())
return cleaned_data
🎉 Congratulations! You've successfully created a Simple Python Transform in Ascend.