Create an Incremental Python Read Component
In this guide, we'll build an Incremental Python Read Component that ingests only new or updated records by leveraging Ascend's Incremental strategy.
Prerequisites
- Ascend Flow
Create a new Component
Begin from your workspace Super Graph view. Follow these steps to create your component:
- Using the Component Form
- Using the Files Panel
- Double-click the Flow where you want to create your component
- Right-click anywhere in the Flow Graph
- Hover over Create Component, then over Read in the expanded menu, and click From Scratch
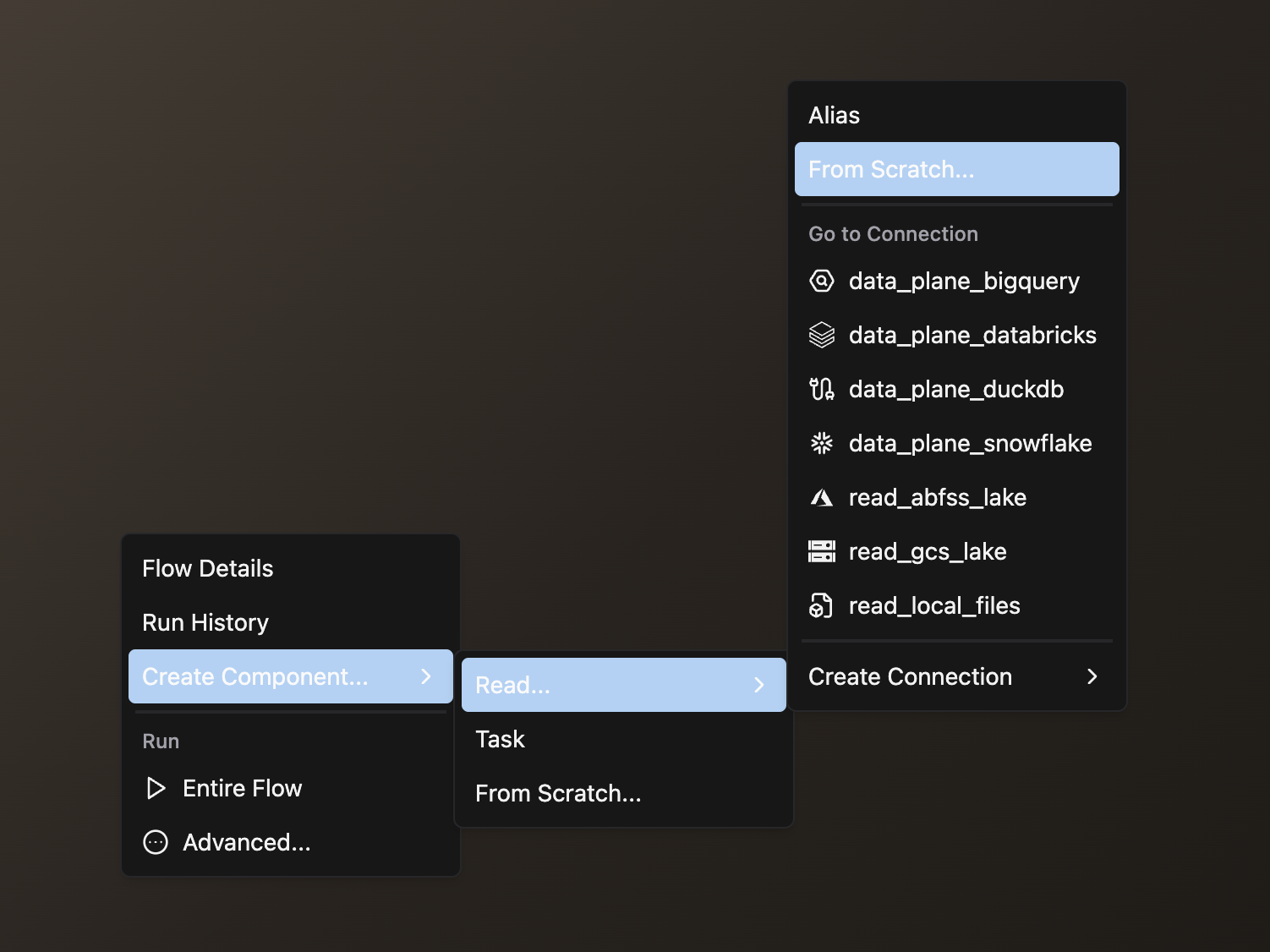
- Complete the form with these details:
- Select your Flow
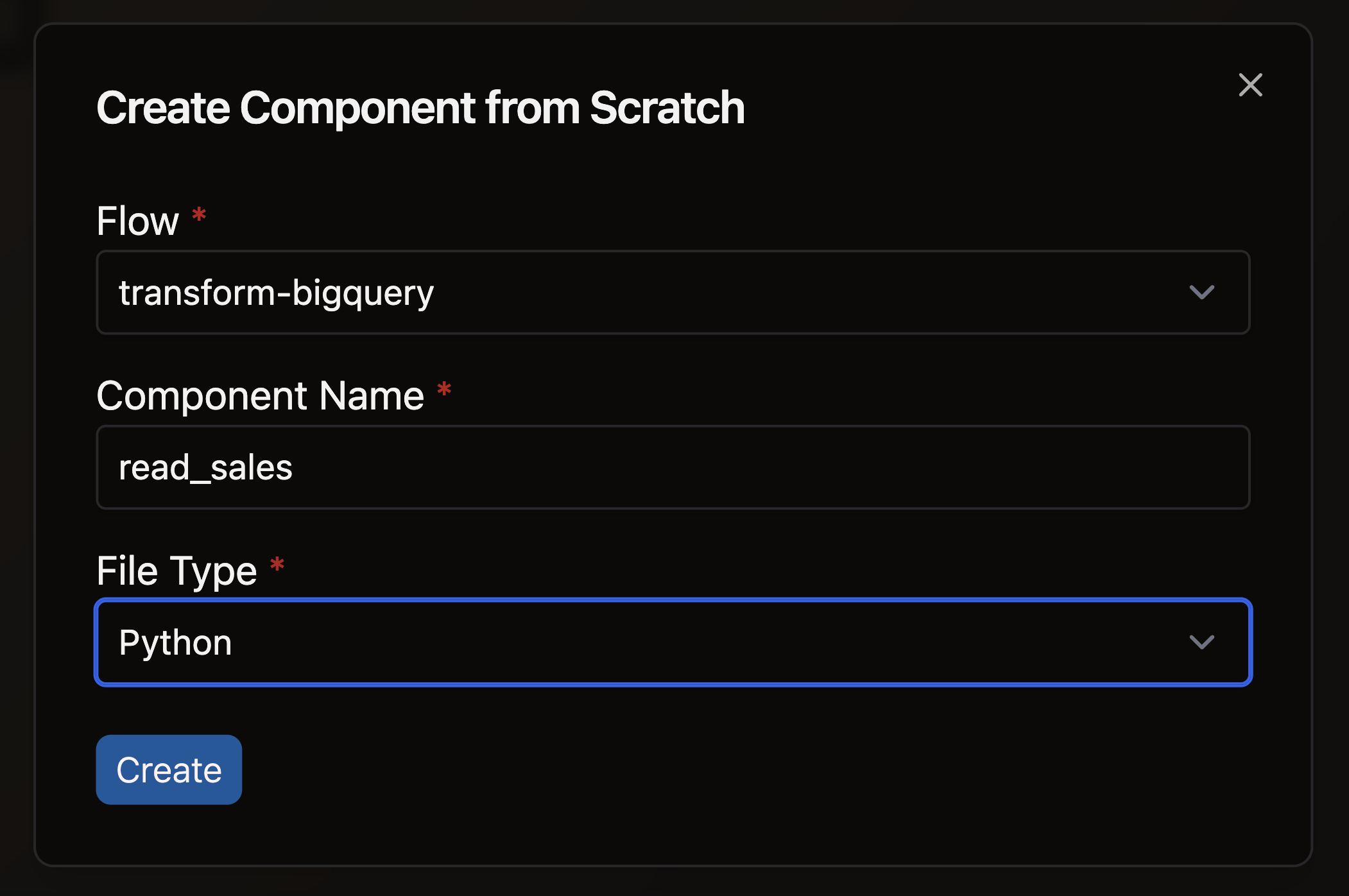
- Enter a descriptive Component Name like
read_sales - Select Python as your file type
- Open the files panel in the top left corner
- Navigate to and select your desired Flow
- Right-click on the components directory and choose New file
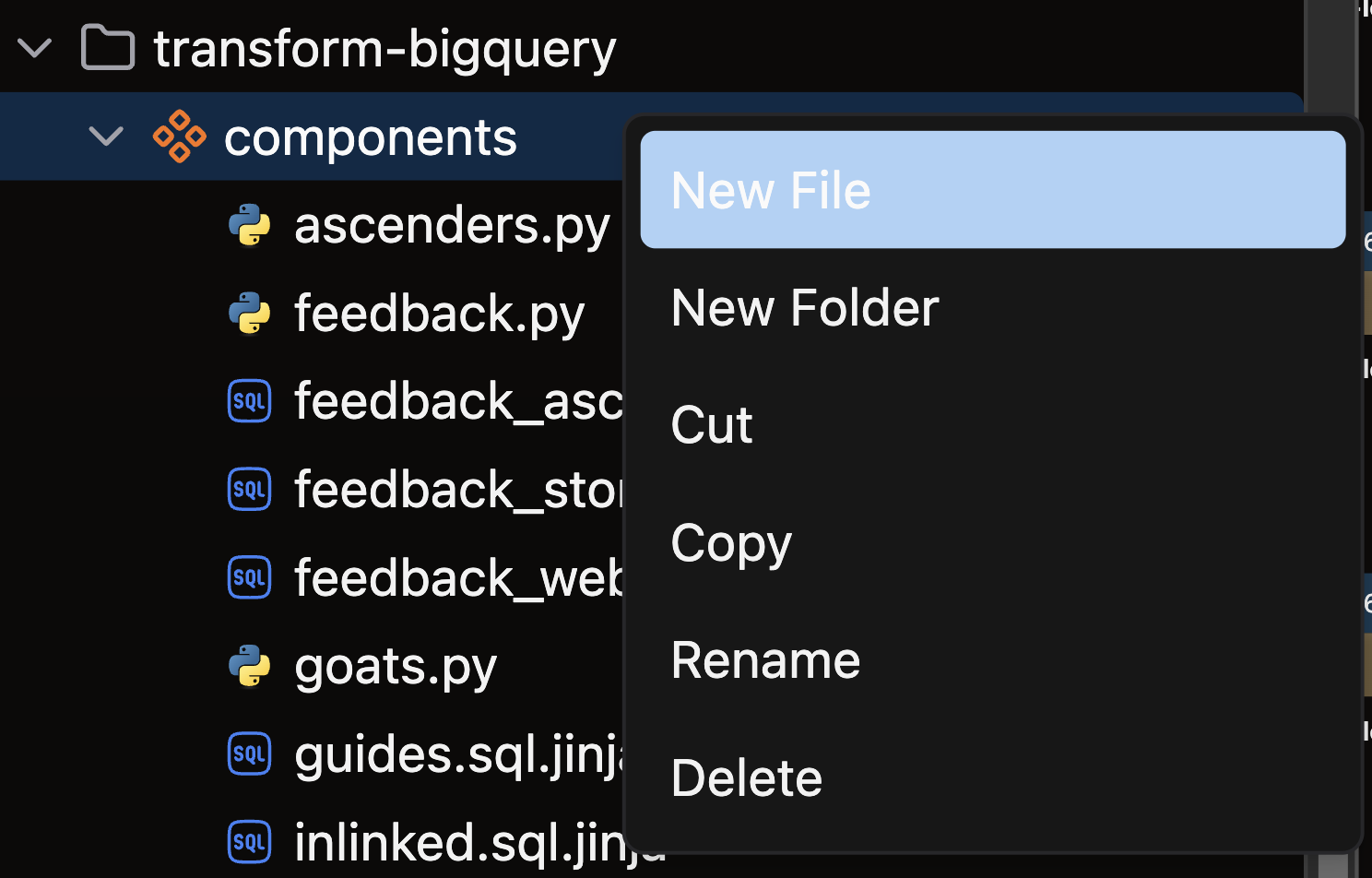
- Name your file with a descriptive name like
read_sales.pyand press enter
Create your Incremental Python Read Component
Structure your Incremental Python Read Component following this pattern, based on our Otto's Expeditions project:
-
Import necessary packages: Include Ascend resources (
read), context handlers (ComponentExecutionContext), data processing libraries (likePolarsorpandas), and logging utilities (log) -
Apply the
@read()decorator with incremental configuration:- Set
strategy="incremental"to enable incremental processing - Choose
incremental_strategy="merge"or"append"based on your data needs - Specify
unique_keyfor merge operations - Set
on_schema_change="sync_all_columns"to handle schema evolution
- Set
-
Define your incremental read function: Implement logic that filters data based on previous state
-
Return structured data: Return the processed data as a dataframe or table
The @read() decorator integrates your function into Ascend's stateful execution framework, automatically managing incremental state and schema updates.
Choose an Incremental Strategy
Ascend offers two incremental strategies: merge and append. Choose based on your data requirements:
| Strategy | Description | When to Use | Required Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Merge | Updates existing records based on a key and inserts new ones | For data that can be updated (user profiles, product info) | unique_key |
| Append | Simply adds new data to existing dataset | For immutable data (logs, events) | None |
For detailed explanations, see our incremental processing reference guide.
Merge strategy example
This example demonstrates the merge incremental strategy using our Otto's Expeditions project:
import polars as pl
import pyarrow as pa
from ascend.application.context import ComponentExecutionContext
from ascend.common.events import log
from ascend.resources import read
@read(
strategy="incremental",
incremental_strategy="merge",
unique_key="id",
on_schema_change="sync_all_columns",
)
def read_inlinked(context: ComponentExecutionContext) -> pa.Table:
"""
Incrementally reads 'inlinked' event data from Otto's Expeditions project.
"""
# Load all available parquet files; Ascend handles merging based on state
df = pl.read_parquet("gs://ascend-io-gcs-public/ottos-expeditions/lakev0/generated/events/inlinked.parquet/year=*/month=*/day=*/*.parquet")
# Retrieve previous data to determine last processed timestamp
current_data = context.current_data()
if current_data is not None:
current_data = current_data.to_polars()
max_ts = current_data["timestamp"].max()
log(f"Reading data after {max_ts}")
df = df.filter(df["timestamp"] > max_ts)
else:
log("No current data found, loading all data")
log(f"Returning {df.height} rows")
return df.to_arrow()
Append strategy example
This example demonstrates the append incremental strategy with timestamp-based filtering:
from datetime import datetime
from ascend.application.context import IncrementalComponentExecutionContext
from ascend.resources import read
# Example data for timestamped incremental append
initial_data = {
"key": [1, 2],
"ts": [datetime(2020, 1, 1, 12, 0), datetime(2020, 1, 2, 12, 30)],
"string": ["a", "b"],
"integer": [1, 2],
}
updated_data = {
"key": [1, 2, 3],
"ts": [
datetime(2021, 1, 1, 12, 0),
datetime(2020, 1, 2, 12, 30),
datetime(2021, 2, 1, 12, 0),
],
"string": ["a", "bb", "c"],
"integer": [1, 2, 3],
}
@read(strategy="incremental", incremental_strategy="append")
def incremental_custom_python_read_append(context: IncrementalComponentExecutionContext):
"""Demonstrates the append incremental strategy with timestamp-based filtering."""
current_data = context.current_data("pandas")
data = initial_data
if context.is_incremental:
# row 1 has an updated timestamp, so it is included in the delta
# row 3 is new and has a timestamp > than the max in the current output
ts_key = "ts"
if context.data_plane_type == "snowflake":
ts_key = ts_key.upper()
max_ts = current_data[ts_key].max()
filtered_data = {key: [val for i, val in enumerate(updated_data[key]) if updated_data["ts"][i] > max_ts] for key in updated_data.keys()}
# Since we are using the append strategy, the updated row 1 will get appended to the existing output.
data = filtered_data
if context.data_plane_type == "snowflake":
# make keys uppercase for Snowflake compatibility
data = {key.upper(): val for key, val in data.items()}
return data
For more examples and advanced options, see our reference guide.
🎉 Congratulations! You've successfully created an Incremental Python Read Component in Ascend.